思考并回答以下问题:
GIN是一个golang常用的Web框架,它对API比较友好,源码注释也很明确,使用起来快速灵活,还有极高的容错率。标题中的路由我们可以简单理解为在浏览器中输入的页面地址,而“树”则是一种优化的数据结构。因为在GIN这个Web框架中的路由树是前缀树,所以我们今天会围绕前缀树来讲解。
什么是前缀树
前缀树其实就是Tire树,是哈希树的变种,通常大家都叫它单词查找树。前缀树多应用于统计,排序和保存大量字符串。因为前缀树能够利用字符串的公共前缀减少查询时间,最大限度地减少不必要的字符串比较。所以前缀树也经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。前缀树拥有以下特点:
- 根节点不包含字符,其他节点都包含字符
- 每一层的节点内容不同
- 从根节点到某一个节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串
- 每个节点的子节点通常有一个标志位,用来标识单词的结束
以小时候查新华字典为例,我们来直观认识一下前缀树。相信大家都用过音序查字法这种查找方式,其操作内容如下:
- 读准字音,根据该字音节确定应查什么字母。
- 在“汉语拼音音节索引”中找到这一字母,在这一字母相应部分找到该字的音节,看清这个音节旁标明的页码。
- 按此页码翻开字典的正文,按四声顺序找出所要查的字。
这整个流程其实可以看做一个粗略的前缀树查找流程,比方说要查找成语“心想事成”中的“心想”两字,在字典中即如下结构:
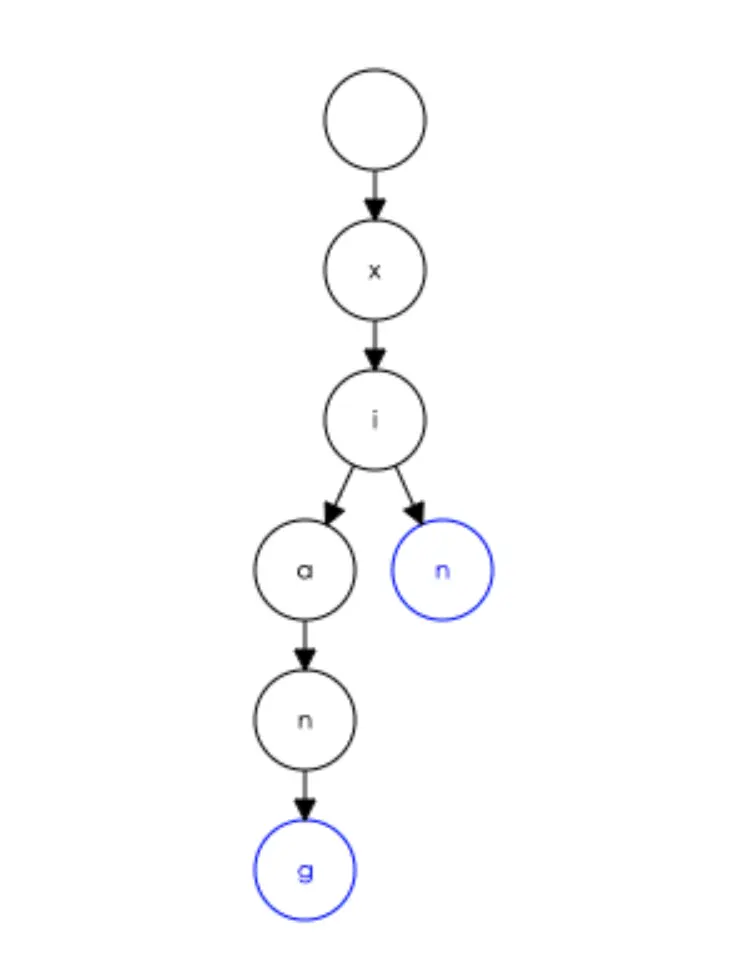
在查找的过程中,我们根据首字母x,找到x当中的xi这一共同部分,然后再根据不同的字母找到所对应的剩余部分。放到前缀树查找上,案例中的“心”对应xi->n,而“想”则对应xi->ang
GIN中的前缀树-紧凑前缀树
GIN中的前缀树相比普通的前缀树减少了查询的层级,比如说上方我们想查找的“心想”其中xi做为共有的部分,其实可以被分配在同一层同一个节点当中而不是分为两部分:
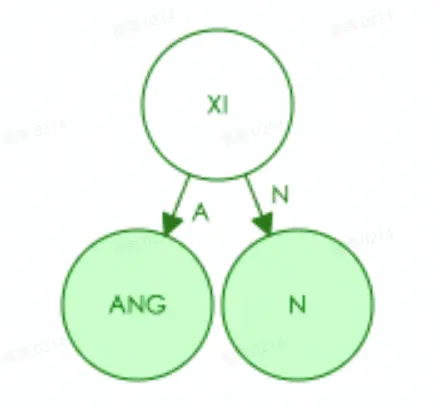
这样的就是紧凑前缀树,同理如果我们有如下四个路由,他们所形成的紧凑前缀树就会是这个样子:1
2
3
4r.GET("/", handle1)
r.GET("/product", handle2)
r.GET("/product/:id", handle3)
r.GET("/product/:name", handle4)
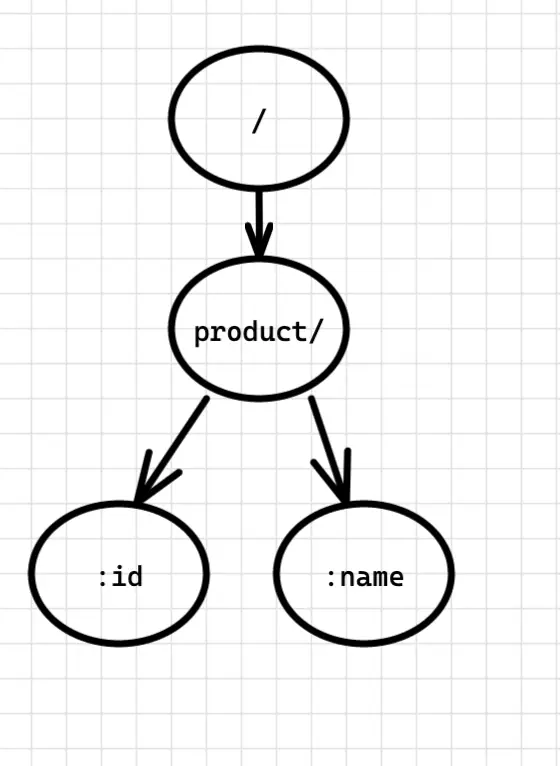
在节点中存储信息
通过上面的内容可以看出,GIN中前缀树整条查询的地址只需通过路由树中每个节点的拼接即可获得。那么GIN是如何完成在这些节点的增加的呢,每个节点中又存放了什么内容?这个问题我们可以通过GIN的源码得到答案。
首先GIN中常用的声明路由的方式如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71func main(){
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.JSON(200, gin.H{
"status":"ok",
})
})
r.Run()
}
// default会初始化一个engin实例
func Default() *Engine {
debugPrintWARNINGDefault()
engine := New()
engine.Use(Logger(), Recovery())
return engine
}
type Engine struct {
RouterGroup
// type RouterGroup struct {
// Handlers HandlersChain
// basePath string
// engine *Engine
// root bool
// }
// 小写私有的,不开放
trees methodTrees
// ...
}
type methodTrees []methodTree
type methodTree struct {
method string
root *node
}
// trees 路由树这一部分由一个带有method 和root字段的node列表维护
// 每个node代表了路由树中的每一个节点
// node所具有的字段内容如下
type node struct {
path string // 当前节点的绝对路径
indices string // 缓存下一节点的第一个字符 在遇到子节点为通配符类型的情况下,indices=''
// 默认是 false,当 children 是 通配符类型时,wildChild 为 true 即 indices=''
wildChild bool // 默认是 false,当 children 是 通配符类型时,wildChild 为 true
// 节点的类型,因为在通配符的场景下在查询的时候需要特殊处理,
// 默认是static类型
// 根节点为 root类型
// 对于 path 包含冒号通配符的情况,nType 是 param 类型
// 对于包含 * 通配符的情况,nType 类型是 catchAll 类型
nType nodeType
// 代表了有几条路由会经过此节点,用于在节点
priority uint32
// 子节点列表
children []*node // child nodes, at most 1 :param style node at the end of the array
handlers HandlersChain
// 是从 root 节点到当前节点的全部 path 部分;如果此节点为终结节点 handlers 为对应的处理链,否则为 nil;
// maxParams 是当前节点到各个叶子节点的包含的通配符的最大数量
fullPath string
}
// 具体节点类型如下
const (
static nodeType = iota // default, 静态节点,普通匹配(/user)
root // 根节点 (/)
param // 参数节点(/user/:id)
catchAll // 通用匹配,匹配任意参数(*user)
)
添加路由则可以通过以下操作:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55// 在创建路由的过程中, 每一个方法都会最终都会被解析后丢给handle函数去处理
func main(){
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/", func(context *gin.Context) {
context.JSON(200, gin.H{
"status":"ok",
})
})
r.Run()
}
func (group *RouterGroup) GET(relativePath string, handlers ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes {
return group.handle(http.MethodGet, relativePath, handlers)
}
func (group *RouterGroup) POST(relativePath string, handlers ...HandlerFunc) IRoutes {
return group.handle(http.MethodPost, relativePath, handlers)
}
// handle函数中会将绝对路径转换为相对路径
// 并将 请求方法、相对路径、处理方法 传给addRoute
func (group *RouterGroup) handle(httpMethod, relativePath string, handlers HandlersChain) IRoutes {
absolutePath := group.calculateAbsolutePath(relativePath)
handlers = group.combineHandlers(handlers)
group.engine.addRoute(httpMethod, absolutePath, handlers)
return group.returnObj()
}
// 路由的添加主要在addRoute这个函数中完成
func (engine *Engine) addRoute(method, path string, handlers HandlersChain) {
// 校验
// 路径必须以 / 开头
// 请求方法不允许为空
// 处理方法不允许为空
assert1(path[0] == '/', "path must begin with '/'")
assert1(method != "", "HTTP method can not be empty")
assert1(len(handlers) > 0, "there must be at least one handler")
// 如果开启了gin的debug模式,则对应处理
debugPrintRoute(method, path, handlers)
// 根据请求方式获取对应的树的根
// 每一个请求方法都有自己对应的一颗紧凑前缀树,这里通过请求方法拿到最顶部的根
root := engine.trees.get(method)
// 如果根为空,则表示这是第一个路由,则自己创建一个以 / 为path的根节点
if root == nil {
// 如果没有就创建
root = new(node)
root.fullPath = "/"
engine.trees = append(engine.trees, methodTree{method: method, root: root})
}
// 此处的path是子路由
// 以上内容是做了一层预校验,避免书写不规范导致的请求查询不到
// 接下来是添加路由的正文
root.addRoute(path, handlers)
}
1 | // addRoute adds a node with the given handle to the path. |
Priority优先级
为了能快速找到并组合完整的路由,GIN在添加路由的同时,会在每个节点中添加Priority这个属性。在查找时根据Priority进行排序,常用节点(通过次数理论最多的节点)在最前,并且同一层级里面Priority值越大,越优先进行匹配。
为何要将9种请求方法放在slice而不是map中
这是因为9个请求方法对应9棵路由树,而GIN对应的所有请求方法都维护了一颗路由树,同时这些关键信息都被包裹在Node结构体内,并被放置在一个数组当中而非map中。这样是为了固定请求数量,同时在项目启动后请求方法会被维护在内存当中,采用固定长度的slice从而在保证一定查询效率的同时减少内存占用。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10type methodTrees []methodTree
func (trees methodTrees) get(method string) *node {
for _, tree := range trees {
if tree.method == method {
return tree.root
}
}
return nil
}
查找路由
路由树构建完毕之后,GIN即可开始正常接收请求。第一步是从ServeHTTP开始解析路由地址,而查找的过程处理逻辑如下:
- 申请一块内存用来填充响应体
- 处理请求信息
- 从trees中遍历比较请求方法,拿到最对应请求方法的路由树
- 获取根节点
1 | func (engine *Engine) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) { |
1 | func (engine *Engine) handleHTTPRequest(c *Context) { |